Drinking Water and Still Thirsty? Here’s What You Might Be Doing Wrong
Introduction: Understanding Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. Water plays an essential role in regulating body temperature, lubricating joints, and supporting various bodily functions. However, many people find themselves drinking plenty of water yet still feeling thirsty. This article explores potential reasons behind this puzzling phenomenon and offers solutions to ensure proper hydration.
Inadequate Electrolyte Balance
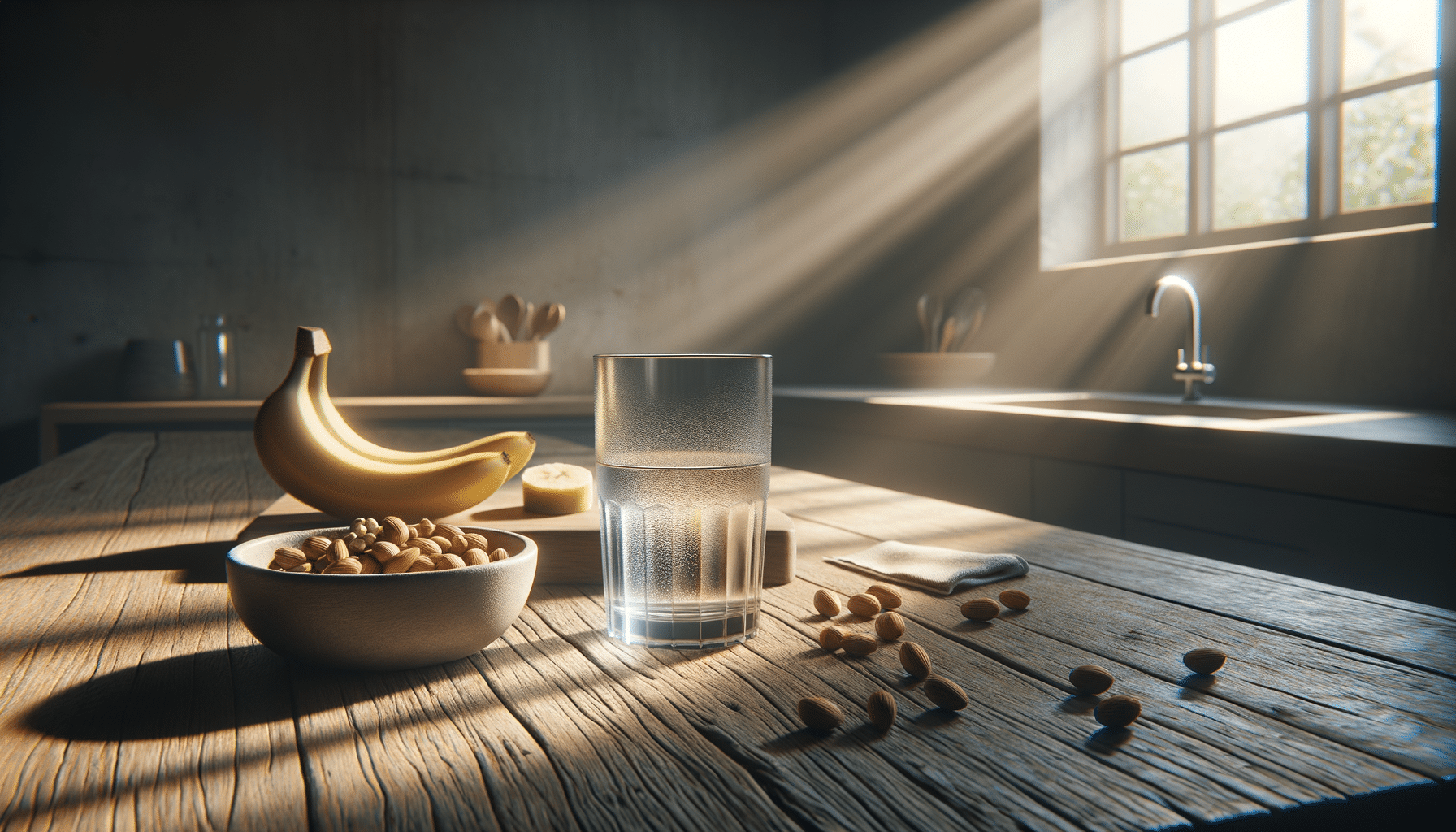
One common reason for persistent thirst despite drinking water is an imbalance in electrolytes. Electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium are vital for maintaining fluid balance within the body. When you consume large amounts of water without replenishing these essential minerals, it can dilute electrolytes, leading to a condition known as hyponatremia. Symptoms may include headache, nausea, and continued thirst.
To address this, consider incorporating electrolyte-rich foods into your diet, such as:
- Bananas and avocados for potassium
- Nuts and seeds for magnesium
- Table salt or electrolyte drinks for sodium
This approach helps keep your body’s fluid balance in check, reducing the likelihood of feeling thirsty despite adequate water intake.
Dehydrating Beverages and Foods
Another factor that can contribute to feeling thirsty is the consumption of dehydrating beverages and foods. Drinks like coffee, tea, and alcohol have diuretic properties, which can lead to increased urine production and fluid loss. Similarly, foods high in salt or sugar can also contribute to dehydration.
To combat this, it’s important to moderate the intake of these dehydrating substances. Opt for water or herbal teas as your primary source of hydration. If you enjoy caffeinated beverages, try to balance them with additional water intake. Reducing the consumption of processed foods high in salt and sugar can also help maintain hydration levels.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Environmental conditions and lifestyle choices can also impact hydration. Hot and humid weather increases sweat production, leading to fluid loss. Similarly, engaging in physical activities without adequate hydration can result in dehydration.
To address these factors, consider the following strategies:
- Increase water intake during hot weather or when exercising
- Wear breathable clothing to reduce sweat loss
- Take regular breaks to hydrate during physical activities
By adapting to your environment and lifestyle, you can better manage your hydration levels and reduce feelings of thirst.
Health Conditions and Medications
Sometimes, persistent thirst may indicate underlying health conditions or the effects of certain medications. Conditions like diabetes, kidney disorders, or thyroid imbalances can affect the body’s fluid regulation, leading to increased thirst.
If you suspect a health condition might be contributing to your thirst, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, some medications, such as diuretics or antihistamines, can cause dehydration as a side effect. Discussing these effects with your doctor can help you manage your hydration more effectively.
Conclusion: Achieving Optimal Hydration
Feeling thirsty despite drinking water can be frustrating, but understanding the potential causes can help address the issue. By ensuring a balance of electrolytes, moderating dehydrating substances, adapting to your environment, and consulting with healthcare professionals when needed, you can achieve optimal hydration. Remember, water is essential, but it’s only part of the equation for maintaining proper fluid balance in the body.